Table of Contents
When people talk about spores, they’re often lumped into one vague category. In reality, spores can represent entirely different research paths, documentation habits, and microscopy goals depending on the species you’re working with. That’s especially true when comparing Lion’s Mane Spores to spores from Psilocybe species.
This guide breaks down the differences in a practical, research-first way. We’re not talking about effects or outcomes. Instead, we’re focusing on how these spores behave under the microscope, how they’re documented, and which type makes more sense depending on what you’re trying to study or catalog.
If you’re building a microscopy library, starting a documentation notebook, or just trying to understand why these two spore types are discussed so differently, you’re in the right place.
Species Background
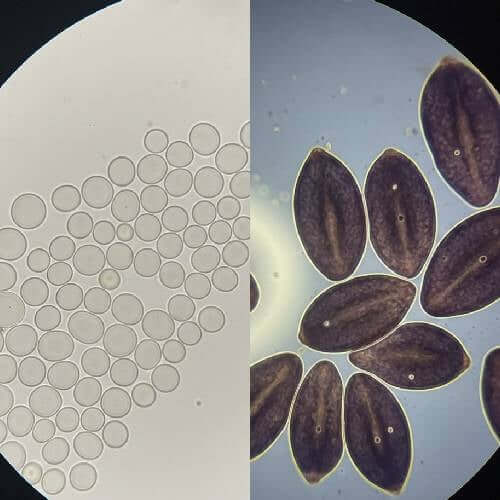
Lion’s Mane and Psilocybe belong to completely different branches of the fungal world, and that difference shows up almost immediately when you look at their spores.
Lion’s Mane comes from the Hericium genus. These fungi are known for their tooth-like structures rather than traditional caps and stems. Their spores are typically white to translucent, and under magnification they tend to appear smooth and subtle. Because of this, Lion’s Mane spores are often studied for structural consistency rather than dramatic visual traits.
Psilocybe species, on the other hand, are classic gilled mushrooms. Their spores are usually darker—often purple-brown to deep violet—and have more visually distinct features. Under the microscope, they tend to stand out quickly, even at lower magnification.
At a high level, you can think of it like this:
- Lion’s Mane spores come from a non-gilled, tooth fungi lineage
- Psilocybe spores come from gilled mushrooms with more complex reproductive structures
- The difference in structure directly affects how they’re examined and recorded
Understanding that background helps explain why these spores are rarely used for the same type of microscopy work.
How Microscopy Focus Differs
One of the biggest differences between Lion’s Mane spores and Psilocybe spores is what researchers actually focus on when viewing them.
With Lion’s Mane, microscopy tends to emphasize uniformity and clarity. The spores are generally smaller and lighter in color, which means they require careful lighting and proper slide preparation to visualize clearly. Researchers often spend more time adjusting contrast, illumination, and focus to bring out subtle details.
Common microscopy focus points for Lion’s Mane include:
- Spore shape consistency across samples
- Surface smoothness and translucency
- Clarity under different magnification levels
Psilocybe spores create a very different experience. Their darker pigmentation makes them easier to spot on a slide, even when the sample density is low. Because of this, microscopy sessions often focus more on distinguishing traits rather than simply making the spores visible.
For Psilocybe spores, microscopy often highlights:
- Color variation between species or samples
- Spore size and shape differences
- Distinctive visual markers that help with identification
In short, Lion’s Mane spores reward patience and fine adjustments, while Psilocybe spores tend to deliver quicker visual feedback under the lens.
Lion's Mane Mushroom Spores

$14.99
Lion's Mane Mushroom Spores Lion's Mane Mushroom Spores Review Unlock the potential of your next microscopy project with our Lion's Mane Liquid Culture. This 10mL syringe is packed with a high-potency strain that’s been sterilized and sealed for your convenience.… read more
Documentation Differences
Because these spores behave so differently under observation, the way they’re documented also tends to differ.
When working with Lion’s Mane spores, documentation often leans toward technical consistency. Since the spores are subtle, researchers usually record precise conditions so observations can be replicated later. Small changes in lighting or magnification can dramatically change what’s visible.
Typical Lion’s Mane documentation may include:
- Exact magnification levels used
- Lighting and condenser settings
- Spore density on the slide
- Notes on clarity and translucence
This style of record-keeping is especially useful if you’re comparing multiple samples over time or building a reference library.
Psilocybe spore documentation tends to look different. Because the spores are visually distinct, notes often focus on comparative traits rather than setup conditions alone. Researchers may still log technical details, but descriptive observations play a larger role.
Psilocybe-focused documentation often includes:
- Spore coloration and intensity
- Shape variations across samples
- Visual differences between known varieties
- Photomicrograph references or sketches
Neither approach is better than the other they’re just suited to different types of research goals.
Who Should Choose Which
Choosing between Lion’s Mane spores and Psilocybe spores isn’t about one being “better.” It’s about what kind of microscopy experience and documentation workflow you want.
Lion’s Mane spores are often a strong fit for people who enjoy methodical observation. If you like dialing in your microscope, adjusting illumination, and carefully teasing out fine details, this species can be very rewarding. It’s also a good option for those building structured notebooks or teaching microscopy fundamentals.
You might gravitate toward Lion’s Mane spores if your goals include:
- Practicing precision microscopy techniques
- Creating repeatable, technical documentation
- Studying subtle morphological features
Psilocybe spores tend to appeal to those who enjoy comparative analysis. Because the spores are easier to visualize, they’re often used for side-by-side comparisons and visual identification exercises. They can also be helpful for learning how different species express unique spore traits.
Psilocybe spores may make sense if you’re interested in:
- Visual comparison between different samples
- Learning identification-focused microscopy
- Building a diverse visual reference collection
Many researchers eventually explore both, using each for different purposes within their broader microscopy work.
Conclusion
At first glance, spores might seem interchangeable, but Lion’s Mane spores and Psilocybe spores offer very different research experiences. One emphasizes subtlety, precision, and technical consistency. The other leans toward visual distinction, comparison, and identification.
Understanding these differences helps set realistic expectations before you ever place a slide under the microscope. It also makes it easier to choose the right spore type for your documentation style, learning goals, and long-term research interests.
Whether you’re drawn to the clean, understated appearance of Lion’s Mane or the bold visual traits of Psilocybe species, the key is approaching each with the right tools, notes, and mindset.
FAQs
Are Lion’s Mane spores harder to see under a microscope?
They can be, especially for beginners. Their lighter color and translucence often require careful lighting and focus adjustments compared to darker spores.
Do Psilocybe spores require less setup time?
In many cases, yes. Their darker pigmentation makes them easier to spot quickly, though proper technique is still important for detailed observation.
Is one better for beginners in microscopy?
That depends on learning style. Lion’s Mane spores are great for learning precision and control, while Psilocybe spores are helpful for visual recognition and comparison.
Can both spore types be documented in the same notebook?
Absolutely. Many researchers keep a single microscopy journal and simply adjust their documentation approach based on the species being observed.





